I’m taking a pause on construction to work all the bugs out of the staging level before building on top of it, so I thought I’d share my method of building manual switch control mechanisms that operate from the fascia. I developed these mechanisms for my last layout, and since they proved to work so reliably, I’m doing the same on my current layout. What I like about these mechanisms is they’re rock-solid, easy to use, and unlike alternatives such as Caboose Industries ground throws, they keep fingers away from the scenicked area of the layout. As an added bonus, using a DPDT slide switch as the “guts” not only gives it a “snap”, but it makes it easy to power frogs and LED indicators if you want them.
The Design
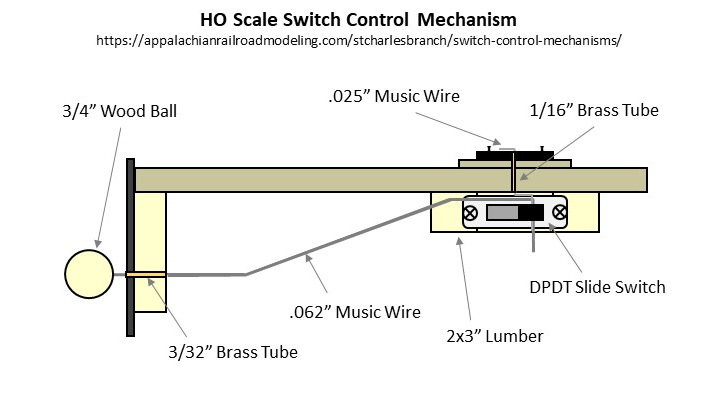
The figure shows most of the relevant parts of the mechanism. It’s essentially a DPDT slide switch mounted to a piece of 2×3″ lumber for the mechanism, a piece of .062″ music wire and a 3/4″ round wood ball for the control arm, a piece of .025″ music wire for the throw, and pieces of 3/32″ and 1/16″ brass tubing where the music wire needs to go through wood.
Making the Parts
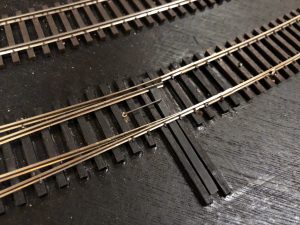
I create the throw first by drilling a snug hole for the piece of 1/16″ tubing about 5/8″ from the throw bar of the switch. I normally drill this dead center between the rails on the frog side of the throw, but if you have benchwork interfering below, you can put this anywhere along the throw bar on either side. I’ve found 5/8″ distance works well with the DPDT switches I use–anything shorter and it won’t throw far enough; anything longer, and the wire is not stiff enough for a reliable throw. I cut a piece of 1/16″ brass tubing just long enough to reach the bottom of the subroadbed while remaining just a fuzz above the ties on top and gently tap it in with a hammer. Next I drill a hole large enough for the .025″ music wire in the throw bar adjacent to the hole for the tubing. I cut a piece of .025″ music wire about 4-5″ long and bend one end to fit perfectly into the throw bar (clipping it to avoid dragging under the throw bar) and dropping into the tube. While holding down the top part of the wire, I reach underneath and bend the other end of the wire as tight as I can by hand opposite the direction of the throw and perpendicular to where the control arm will go–it doesn’t matter that the bell crank is in line with the throw; it matters that it’s perpendicular to the direction the control arm will need to move. Finally, I use a pair of needle-nosed pliers to bend the wire toward the ground about 3/16″ from where it exits the bottom of the tube. The bell crank is now complete, and you should be able to easily throw the switch by moving the bottom of the wire back and forth.
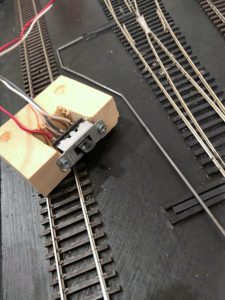
Next I build the mechanism. First I solder feeders onto the DPDT switch–I use red and white for the connections to the track bus and gray or blue in the center for the connection to the frog. Next I cut a piece of 2×3″ lumber about 2 1/2″ long (you can use any size, but smaller will be more delicate, and larger will be tougher to fit around benchwork). Then I a notch about 1″ deep just wide enough for the DPDT switch to fit. At this point I designate a “top” of the mechanism and install the DPDT switch with small wood screws. With the mechanism placed between the throw and the frog, the feeders should be REVERSED from the normal orientation of your track bus. In other words, my track bus is normally oriented red/black-front, white-back, so I install my DPDT switch with the white feeder in front. Finally, I drill two holes through the slide portion of the DPDT switch, one just big enough for the .062″ control wire and the other closer to the tip of the switch for the .025″ throw wire. I’ve found drilling both holes with the smaller bit and then enlarging one prevents the plastic from breaking. I put a little countersink into the top of the holes by spinning an X-Acto knife in them to make it easier to insert the wires. NOTE: my switches are hollow inside which makes it a bit of a pain to insert the wires sometimes–it just takes a litte patience. I finish by drilling and countersinking two holes where I want the screws for mounting it to the layout will go.
The next step is the control arm. First I decide where I want the control knob on the fascia. For me, I use a simple track diagram on the fascia with switches drawn in (more on this in a later post), so I draw the diagram first, then drill the hole that will tightly fit the 3/32″ brass tube perpendicular to the ground and aimed toward the end of the throw crank under the layout. Then I cut the 3/32″ brass tubing to fit just through the fascia and 2×3″ board edging the layout. In some spots, there is no board, so I’ll glue a square piece of 2×3″ lumber behind the fascia to ensure adequate support. There might also be other lumber between the fascia and the switch. If its a fairly short distance (<12″), I’ll drill a 5/8″ hole where the control arm will go through. If it’s a longer distance, I’ll drill a second hole for 3/32″ tubing in line with the first–this isn’t tough to do if you take a piece of straight .062″ wire, push it through the fascia tube and mark where it hits the intervening lumber. The straigher you make these two tubes, the smoother the mechanism will be. Finally, I bend a control arm. Starting at the switch end, I bend the last 1″ 90 degrees toward the ground where it will go through the slide switch, then I make a slight bend downward about 1″ from the 90 degree bend toward the fascia hole, then another bend about 1 1/2″ from where it will go through the 3/32″ tubing. The sharpness of the anlged portion depends on how much room you have between the switch and fascia and how far down on the fascia your control knob will be. The shallower the bends, the more solid and reliable the mechanism will be. I cut it with a Dremel tool and cutoff disk (enjoy the fireworks!) so it will protrude about 1 1/2″ through the fascia and file the burrs off the end.
Mounting the Mechanism
This part is straightforward, but it can be tricky and sometimes frustrating to get the switch is exactly the right spot–it requires some experience and skill to get it right, and that experience and skill requires some misfires and mistakes to gain. I first install two 1 1/4″ drywall screws into the mechanism mounting holes with about 3/32″ of the tip sticking through–this gives a way for the mechanism to grab the subroadbed a little while you’re placing it. Then I insert the control arm through the DPDT switch and run the other end through the 3/32″ tube(s) and out the fascia. Next I place the mechanism onto the .025″ bell crank (this part can be tricky and frustrating if the wire and holes don’t line up well). Once everything is inserted, I place the DPDT slide in the middle position and do the same with the throw topside–with both of these in the middle position and the DPDT slide direction in line with the control arm, I press the mechanism into the subroadbed and hold it in place. While holding the mechanism in place under the layout, I’ll try work the mechanism to ensure it throws snugly to both sides. This is a matter of trial-and-error, but once I’m satisfied, I’ll put one of the screws into the subroadbed. Inevitably, it will leave a gap between the mechanism and subroadbed because I wasn’t able to pre-drill the hole. . . no worries. Then I’ll start the second screw, go back to the first and back it out then put it back in to cinch it up, then do the same to the second. If all has gone well, the control arm will easily push the slide switch to both limits, and the throw will push the point rails snugly to each stock rail. If not, back out the screws and try again!
Once I’m satisfied that the mechanism is where it needs to be, and everything is operating smoothly, the last step is to install the control knob. I first push the control arm wire in, then cut it off with the Dremel about 5/8″ from the fascia and file smooth. Then I drill a hole straight into and about 2/3 of the way through the round wood ball. After moistening the wire and ball, I add a drop of Gorilla Glue to the wire and place the wood ball onto the wire. It should be tight enough that you have to twist it on. I like for the control knob to sit about 3/16″ from the fascia when the knob is pushed in. Work the switch a few times while the glue is wet to make sure it feels right where you’ve placed it, then let it dry. Connect the feeder wires to the track bus and the third wire to the frog and the switch mechanism is complete! While it sounds like a lot of steps, if you mass produce the 2/3″ mounts and DPDT switches with pre-drilled holes and wires pre-soldered, you can install 3-5 mechanisms in an hour.
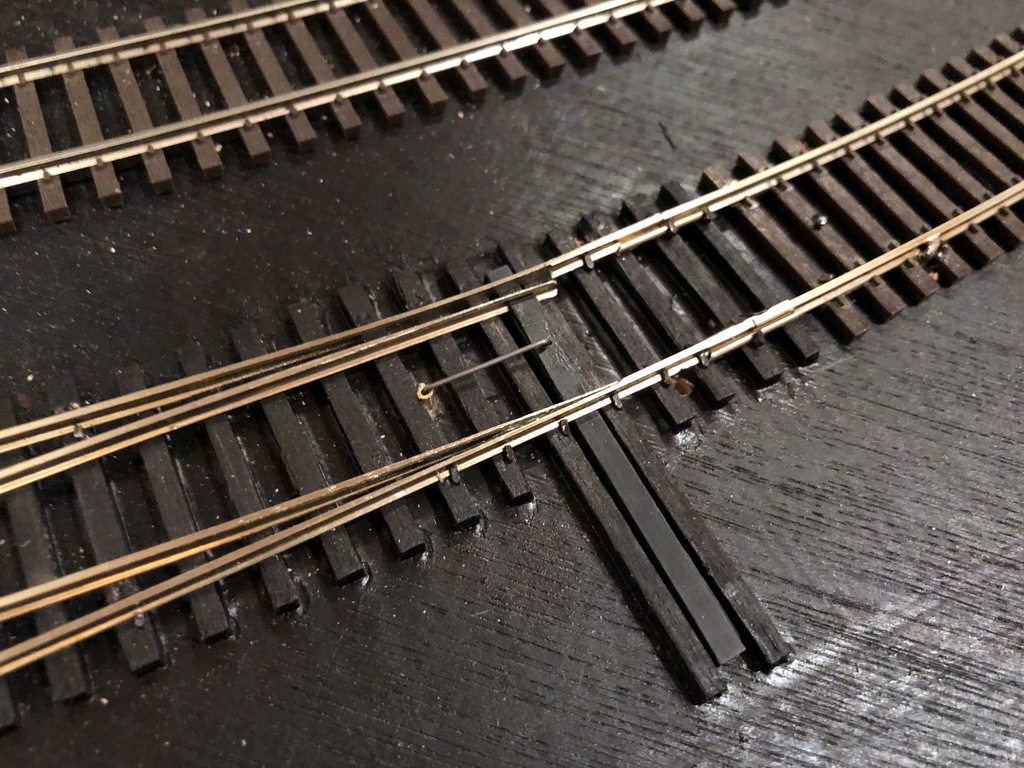
The top portion of the throw bell crank made from music wire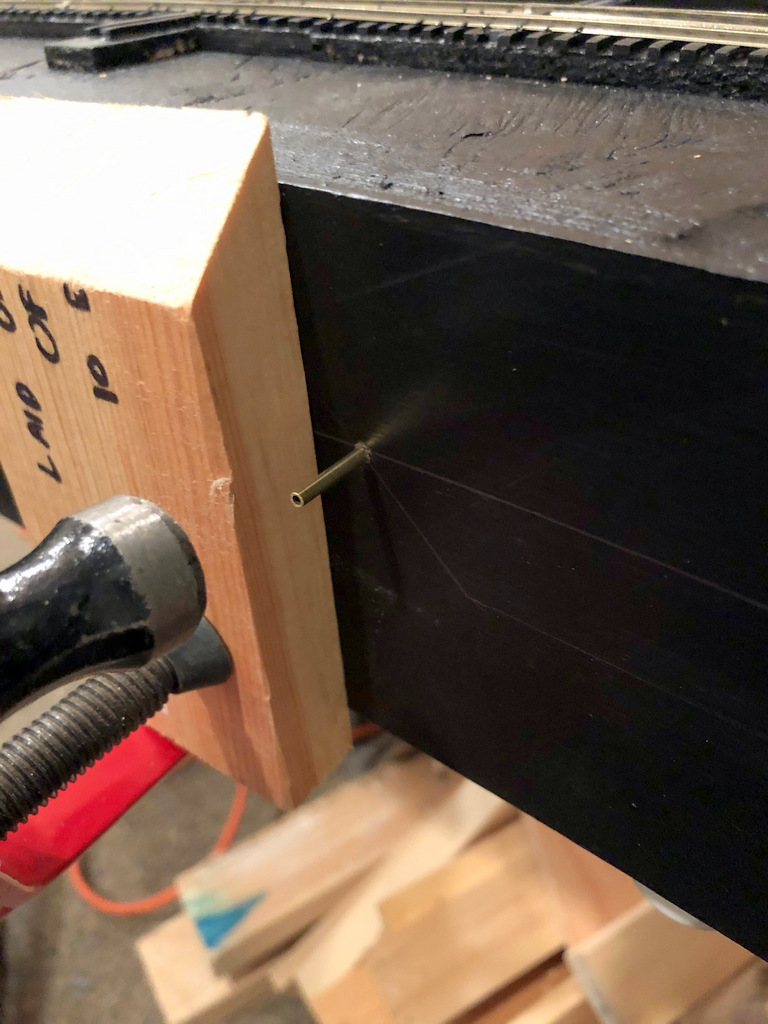 
Hammering the 3/32″ brass tube through the fascia–the tubing should fit snugly. the board and clamp are holding a piece of 2×3″ lumber onto the back side of the fascia to add stability. 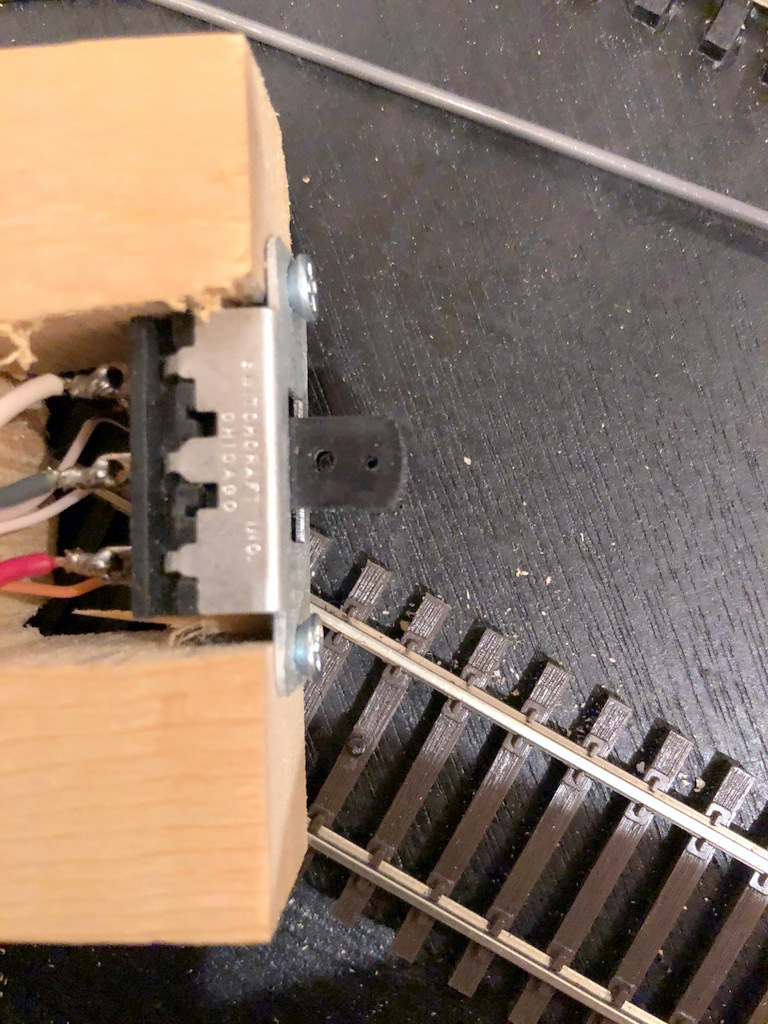
Two holes drilled into the DPDT switch lever, one for the control arm and one for the bell crank 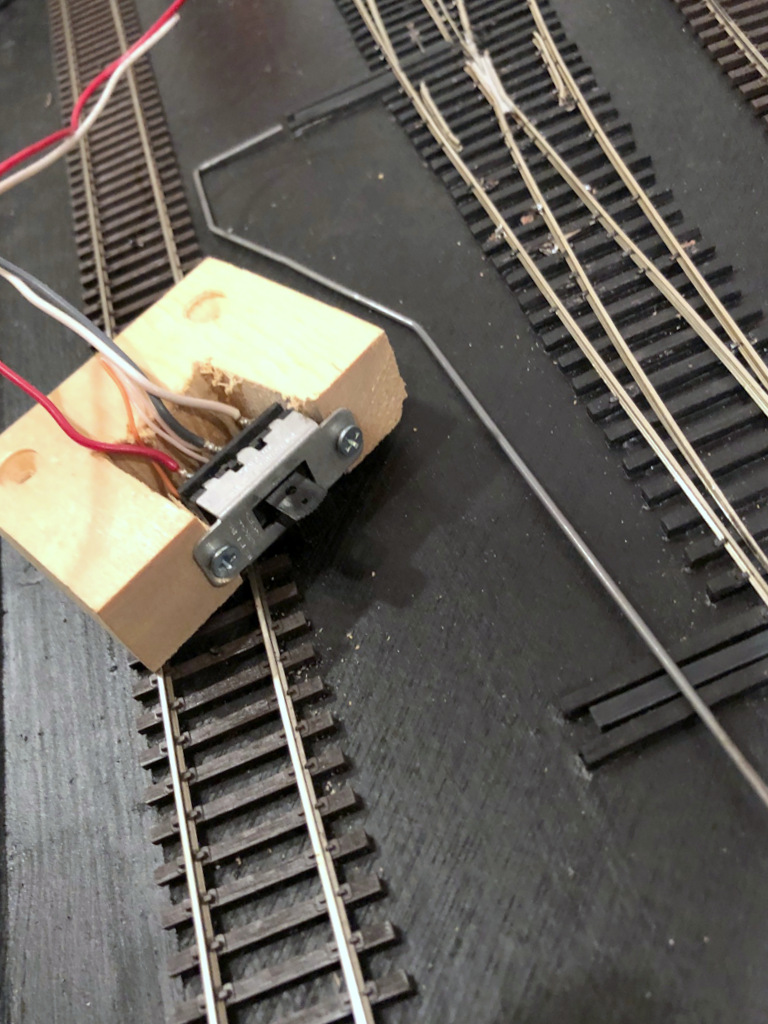
Switch mechanism ready for mounting sitting next to its control-arm wire 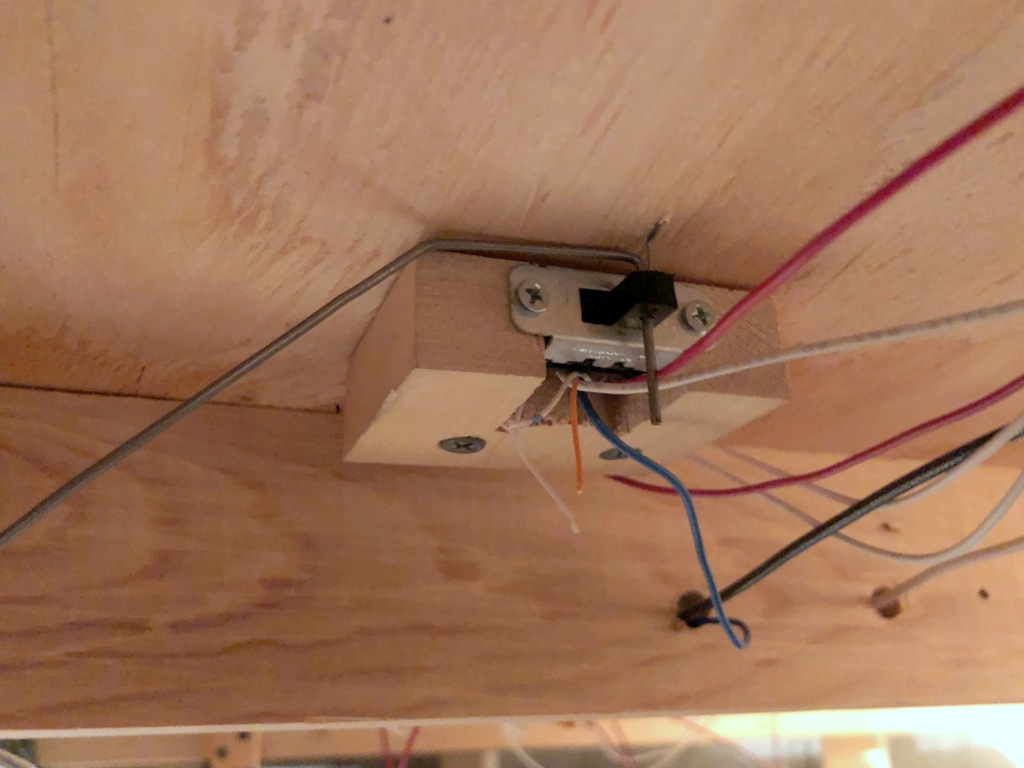
Here’s what a completed installation looks like under the layout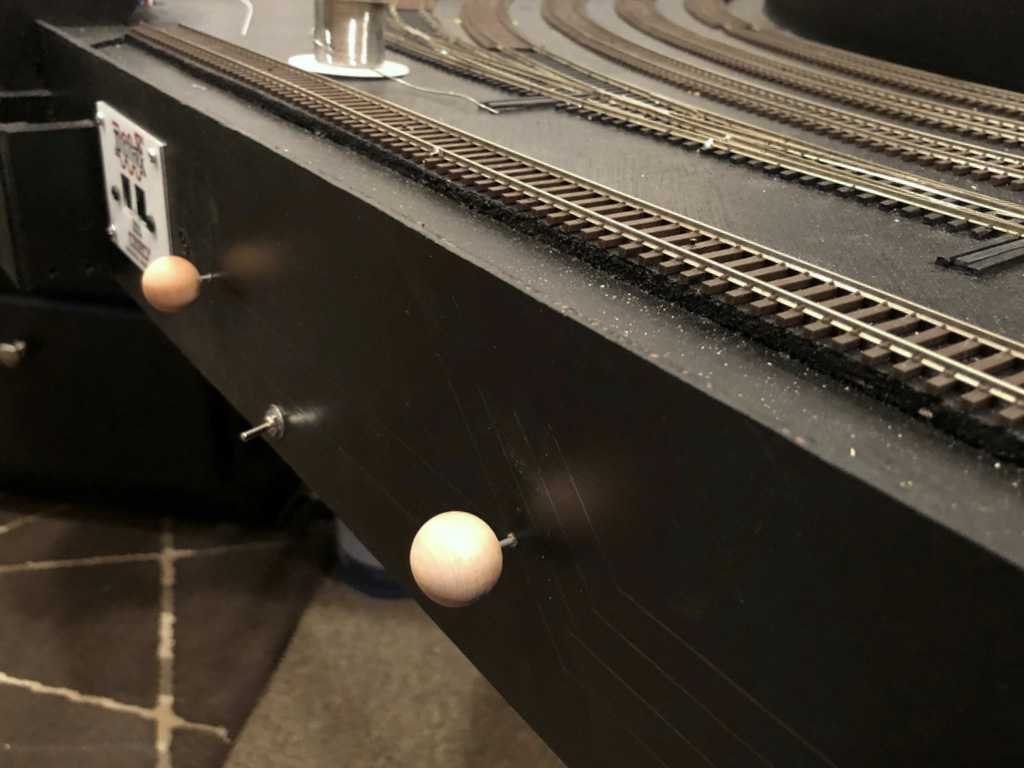 
How the completed switch mechanism looks on the fascia


This Switch mechanism’s is pretty awesome. That would save me alot on tortoise switch motors. I already downloaded the schematic (thank you for that drawing.) Keep up the good work.
Peter, I’ve been really happy with these, so I definitely recommend trying them out! You also can’t beat the cost if you buy your DPDT switches in bulk—probably around $1 in parts here. Since all the switches on the St Charles Branch were locally controlled by the crews, it was an easy decision to go manual on everything. A little tougher if you’re going to need some switches controlled by a dispatcher or computer.